This dataset includes data for 39 species of mammals distributed over 13 orders. The data were used for analyzing the relationship between constitutional and ecological factors and sleeping in mammals. Two qualitatively different sleep variables (dreaming and non dreaming) were recorded. Constitutional variables such as life span, body weight, brain weight and gestation time were evaluated. Ecological variables such as severity of predation, safety of sleeping place and overall danger were inferred from field observations in the literature.
Format
A data frame with 62 observations on the following 11 variables.
- species
Species of mammals
- body_wt
Total body weight of the mammal (in kg)
- brain_wt
Brain weight of the mammal (in kg)
- non_dreaming
Number of hours of non dreaming sleep
- dreaming
Number of hours of dreaming sleep
- total_sleep
Total number of hours of sleep
- life_span
Life span (in years)
- gestation
Gestation time (in days)
- predation
An index of how likely the mammal is to be preyed upon. 1 = least likely to be preyed upon. 5 = most likely to be preyed upon.
- exposure
An index of the how exposed the mammal is during sleep. 1 = least exposed (e.g., sleeps in a well-protected den). 5 = most exposed.
- danger
An index of how much danger the mammal faces from other animals. This index is based upon Predation and Exposure. 1 = least danger from other animals. 5 = most danger from other animals.
References
T. Allison and D. Cicchetti, "Sleep in mammals: ecological and constitutional correlates," Arch. Hydrobiol, vol. 75, p. 442, 1975.
Examples
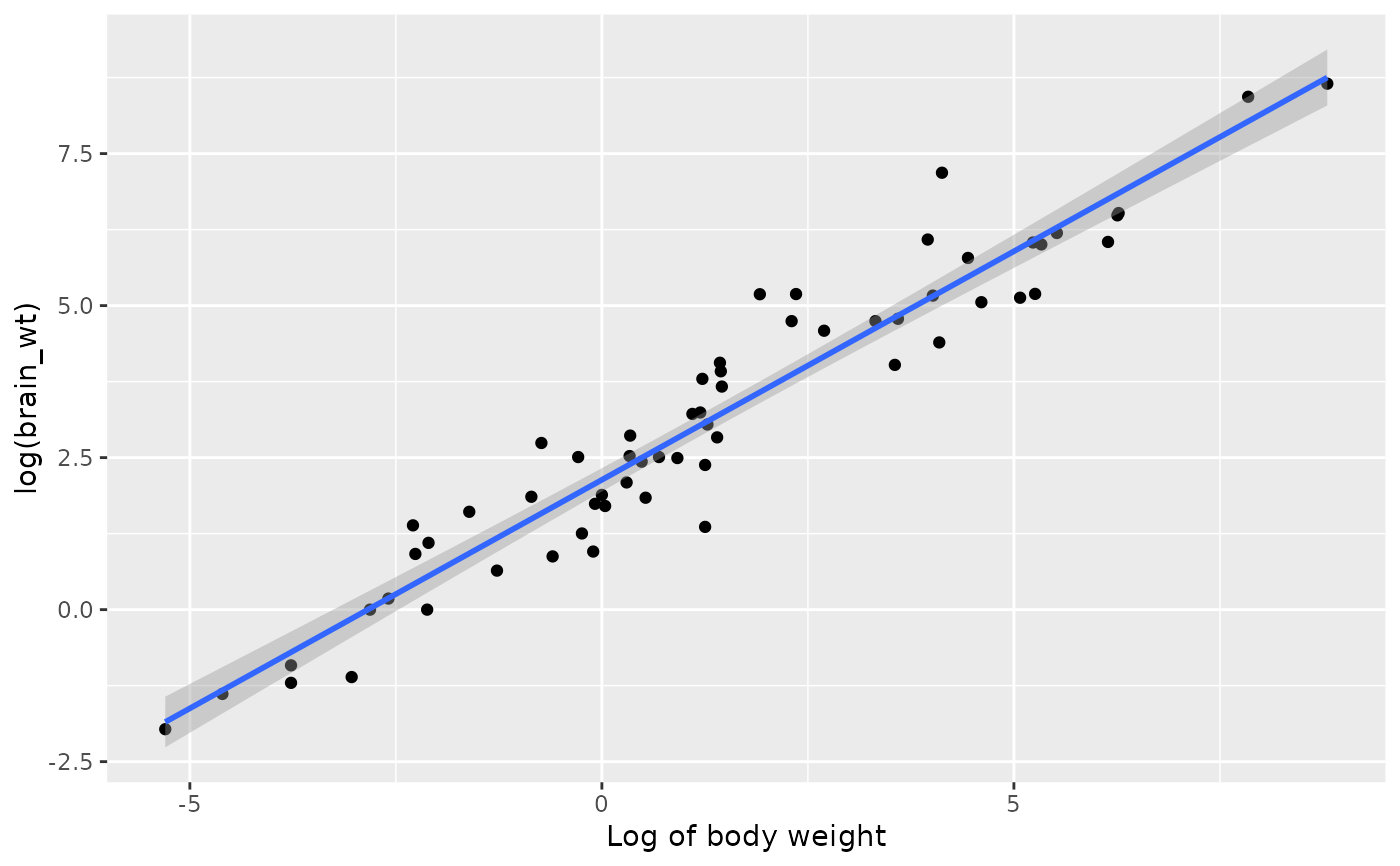
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(mammals, aes(x = log(body_wt), y = log(brain_wt))) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm") +
labs(x = "Log of body weight", x = "Log of brain weight")
#> `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'